Which Represents a Short-term Storage for Carbon
Formation and destruction of fossil fuels and sediments containing organic carbon. Limestone rocks quarried at Earths surface.
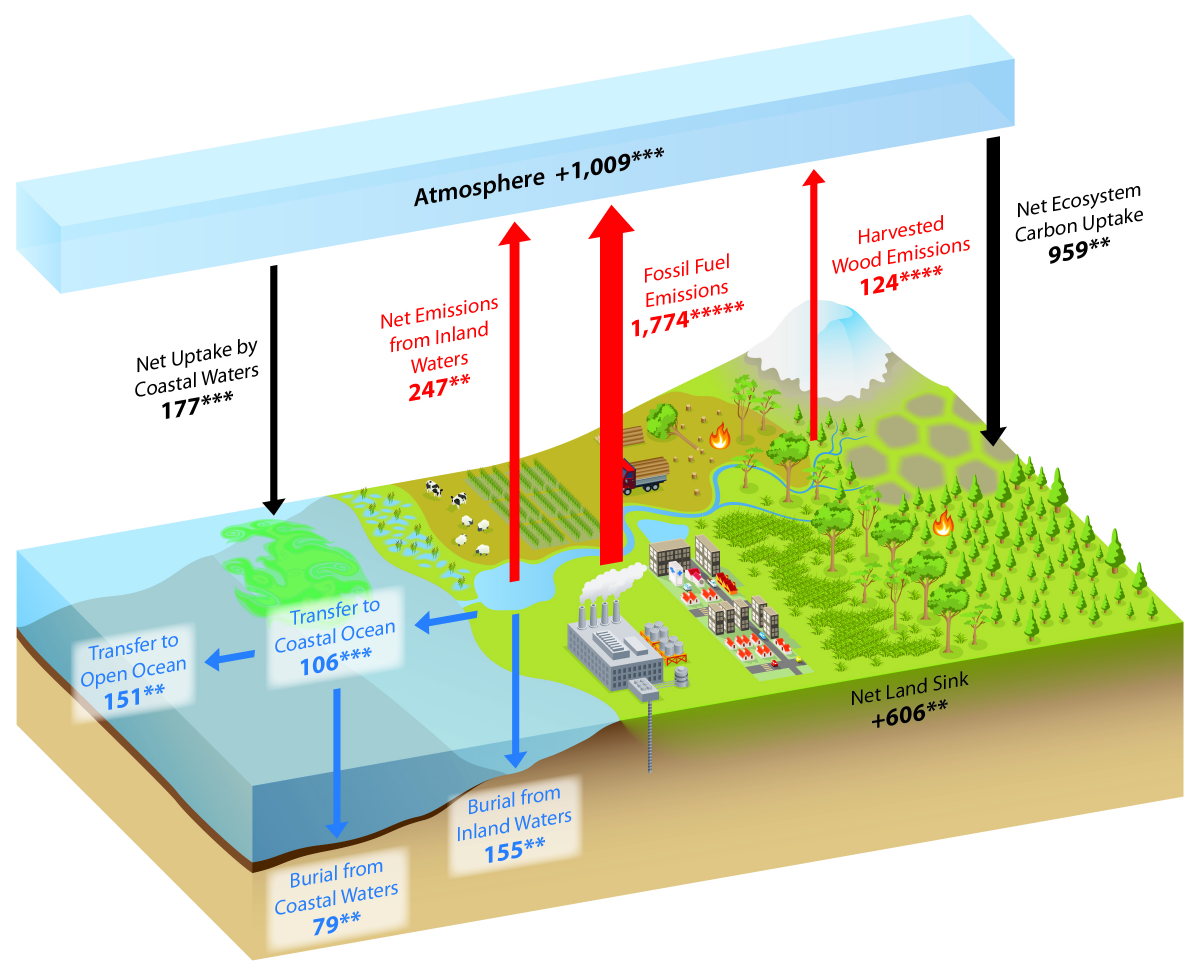
What Is The Carbon Cycle What Is The Science Behind It United States Carbon Cycle Science Program
Short term organic carbon cycle.

. It can be represented succinctly by the general-. Which represents a short-term storage for carbon. A process of burning something into the air.
The Carbon Cycle and Long-Term Carbon Storage. Interactions between atmosphere and biosphere terrestrial and marine components. Where carbon is stored temporarily.
The amount of carbon in the atmosphere is surprisingly small. This is called short term storage because the carbon is locked up for the life of a tree and only released on the death of the tree. To tackle these questions we first need a little background.
Carbohydrates stored in fruits and vegetables. Short term This type occurs within a relatively short period of time. It takes months to centuries to recycle carbon dioxide.
Long term This type takes thousands of years to occur. The excess carbon from the short-term cycle is stored for a long time before they are released. The production of food energy by land plants.
The long term storage of carbon dioxide. But far and away the most carbon on Earth is stored in a surprising place. Coal formed from plants that lived long age C.
In the short-term reservoir carbon is stored in the atmosphere oceans and biosphere with the ocean containing the largest amount of carbon. Used in animals as short-term energy storage. Collectively all of the major pools and fluxes of carbon on Earthcomprise.
Starting now carbon capture and storage CCS methods must sequester about 125 Gt of CO 2 by 2100 National Academies of Sciences Engineering Medicine 2019. Carbon storage in living vegetation and soils. The Slow Carbon Cycle.
The ocean and the atmosphere serve as long-term storage areas for carbon and other nutrientsWhat are these storage areas called. Simplest carb or simple sugars. Stored in muscle cells and used as a source of energy.
Sedimentary rocks and fossil fuels. What is the largest pool of carbon on the planet. It is named as such because it takes just days months or years for carbon to flow across the various carbon reservoirs.
Carbon between rocks and the surficial system which con-sists of the ocean atmosphere biosphere and soils. Its in organic matter in the soil and its in rocks. A Coral reefs formed from calcium carbonate.
Annual plants or for thousands of years for mature hard wood forests. Soils represent a short to long-term carbon storage medium and contain more carbon than all terrestrial vegetation and the atmosphere combined. Where carbon is released.
A Decarbonization Win-Win That Produces Clean Hydrogen And Clean Carbon Black. On average 10 13 to 10 14 grams 10100 million metric tons of carbon move through the slow carbon cycle every year. Why is carbon dioxide a trace gas about 367 ppmv rather than making up most of the atmosphere as is the case for the sibling planets of Earth Venus and Mars.
And are chemical signaling molecules hormones - can hold more than twice the long - term energy amount than carbohydrates - 4 types. 3 Humans are now releasing carbon dioxide from long term stores faster than any time in the past. Log in for more information.
Calcium ions react with carbonate to produce calcium carbonate - deposited on ocean floor where it is lithified to form limestone - most calcium carbonate is made by shell-building organisms which sink to the seafloor after death and cement together as layers that turn to rock. Through a series of chemical reactions and tectonic activity carbon takes between 100-200 million years to move between rocks soil ocean and atmosphere in the slow carbon cycle. The ocean and the atmosphere serve as long-term storage areas for carbon and other nutrientsThese storage areas are called RESERVOIRS.
Reservoirs fossil fuels biostorages compounds Weegy. Theres estimated to be 38000 to 40000 billion metric tons of carbon in the ocean itself with a whopping 66 million to 100 million-billion metric tons of carbon in marine sediments and sedimentary rocks. Through photosynthesis the inorganic carbon in carbon dioxide plus water and energy from sunlight is transformed into organic carbon food Figure above with oxygen given off as a waste product.
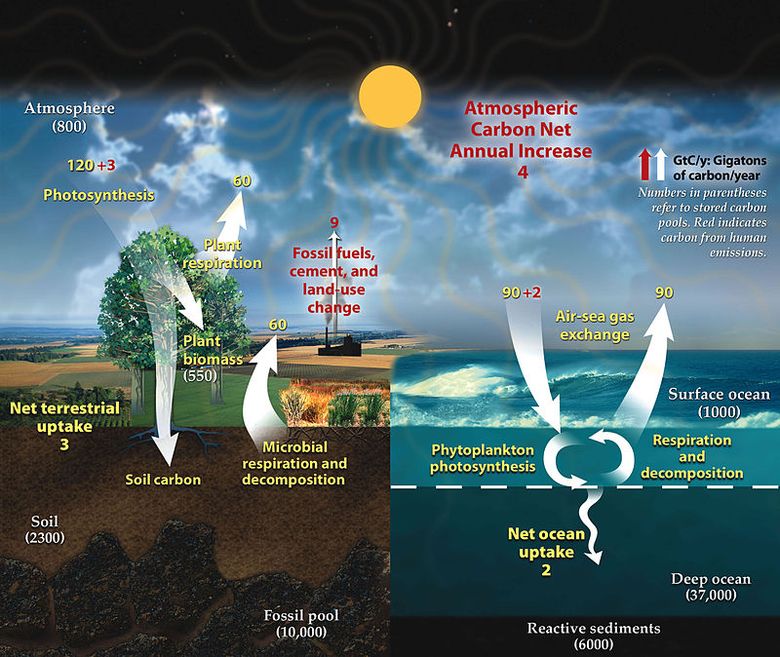
Biomass that makes up all. POOLSFLUXES AND A WORD ABOUT UNITS. Plant litter and other biomass including charcoal accumulates as organic matter in soils and is degraded by chemical weathering and biological degradationMore recalcitrant organic carbon polymers such as cellulose hemi.
Hydrogen represents a potential clean fuel and source of long-term storage but producing it without emissions at. Atmospheric oxygen combines with glucose to form water and carbon dioxide. Polysac made of 1000s of glucose subunits linked together.
Two possible methods for long-term CO 2 storage are underground sequestration in sedimentary formations and carbon mineralization National Academies of Sciences Engineering Medicine 2019. Two long term storage locations for carbon on Earth are. A very small amount of organic material is buried under sediment and taken out of the short-term carbon cycle that cycles carbon between living organisms the atmosphere and the surface of the oceans.
What keeps it at a low level. Long term organic carbon cycle. Fats triglycerides phospholipids steroids ans waxes.
Used in plants as long-term energy storage. The process by which cells produce energy from carbohydrates. The short term cycling of carbon begins with carbon dioxide CO 2 in the atmosphere.
-Much more branched than starch. - Used for long - term energy storage building cell membranes phospholipids insulation and cushioning of internal organs. The long-term carbon cycle is the main controller of the concen-tration of atmospheric carbon dioxide and along with the sulphur cycle atmospheric oxygen over a geological timescale12.
Sediments in the deep ocean. In order to understand how carbon is cycled and how atmosphericCO2 will change in the future scientists must carefully study theplaces in which carbon is stored pools how long it resides thereand processes that transfer it from one pool to another fluxes. Coal is long term storage.

Pin On Macro Micro Up Close And Personal

Global Carbon Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
For132 Fr188 Wood To Energy Climate Change And Carbon

Global Carbon Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
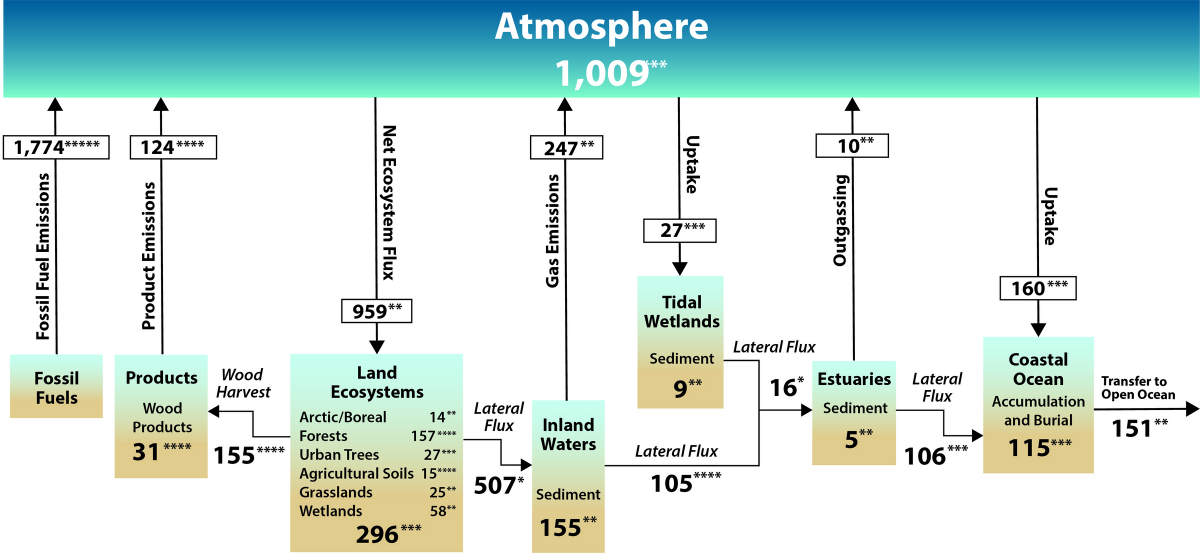
What Is The Carbon Cycle What Is The Science Behind It United States Carbon Cycle Science Program
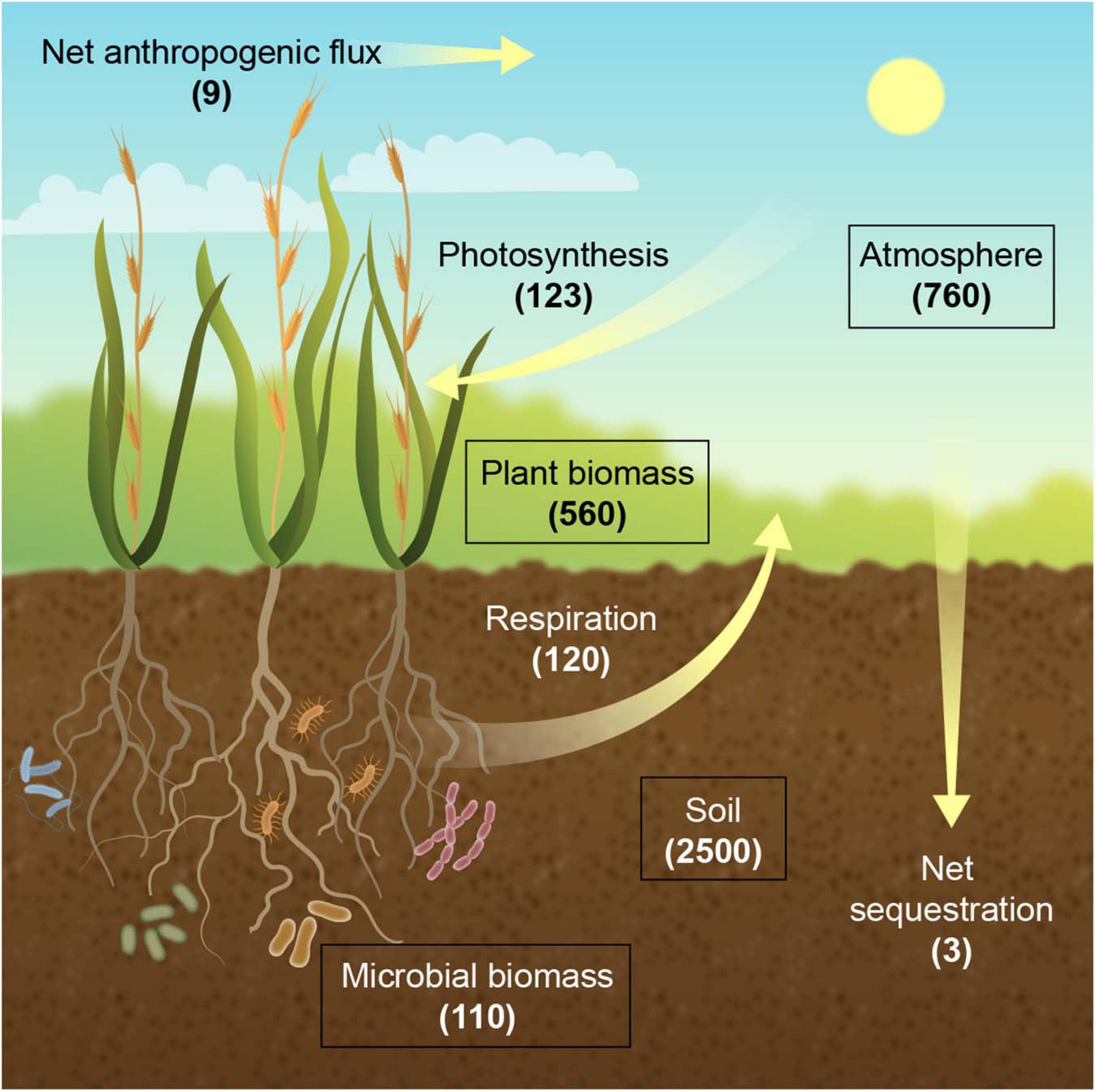
Frontiers Crops For Carbon Farming Plant Science
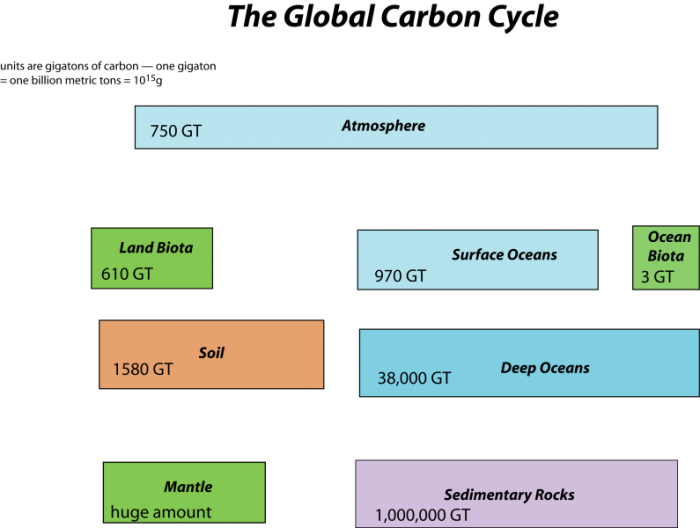
Overview Of The Carbon Cycle From A Systems Perspective Earth 103 Earth In The Future

Global Carbon Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
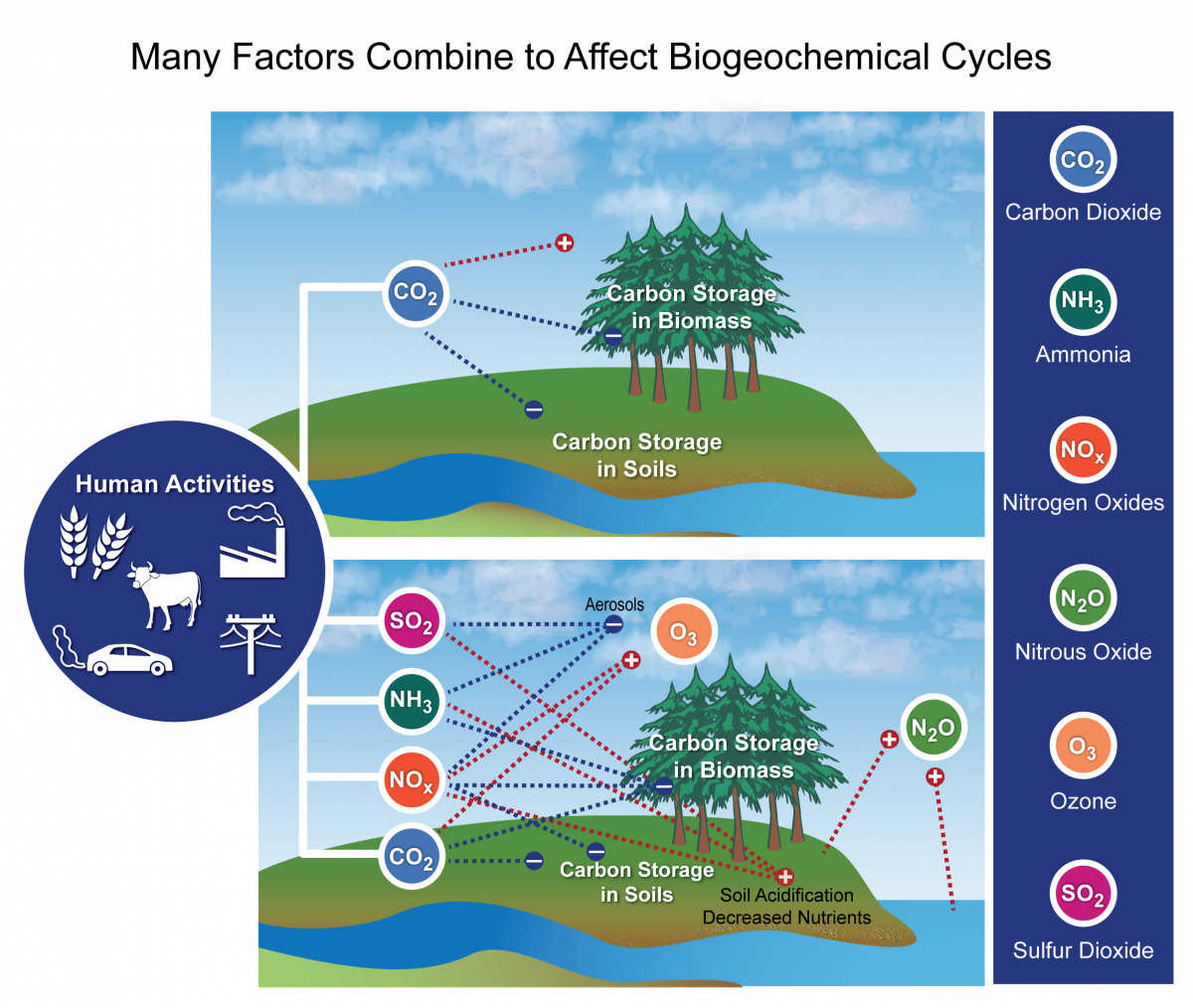
What Is The Carbon Cycle What Is The Science Behind It United States Carbon Cycle Science Program
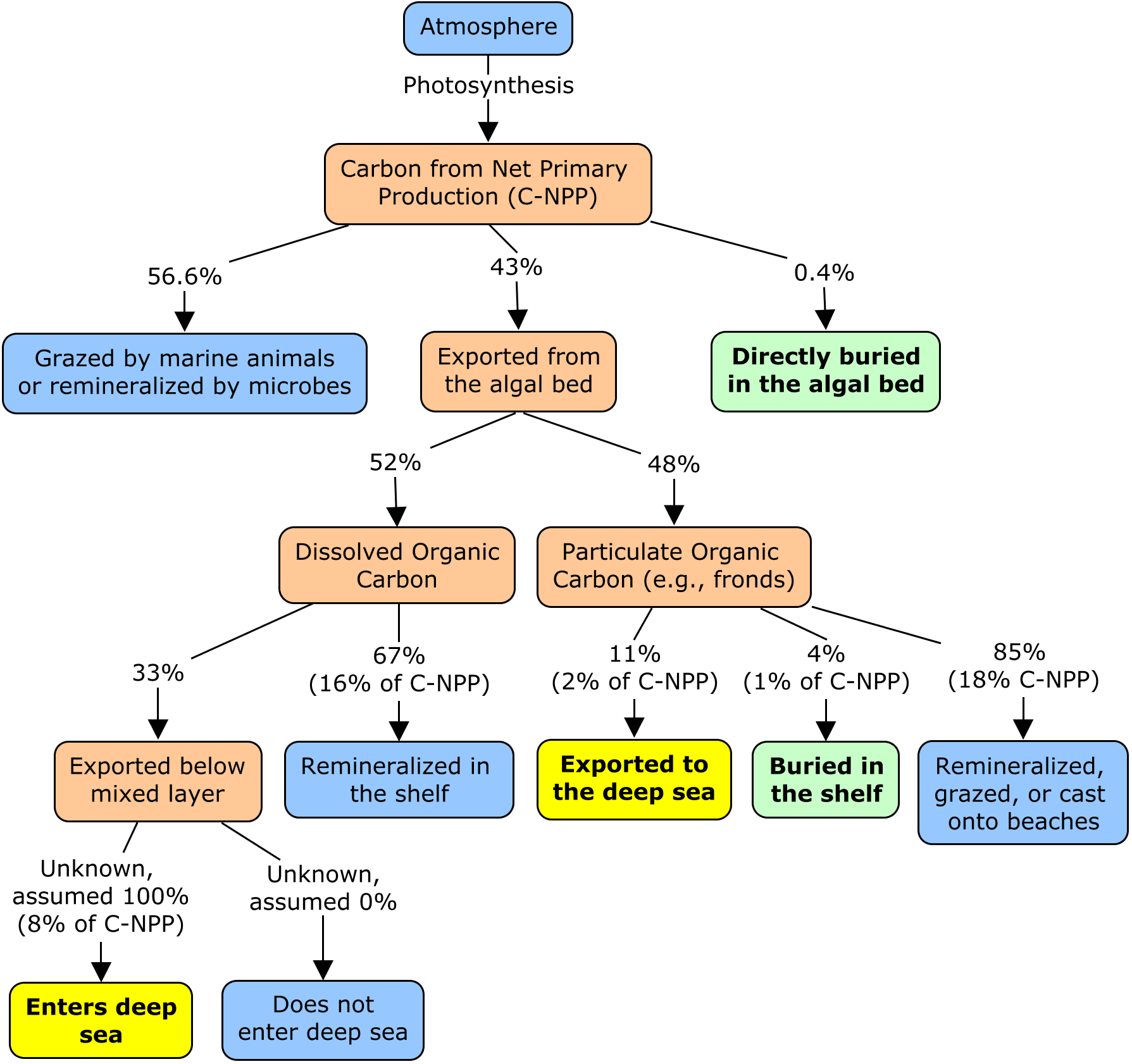
Kelp And Carbon Sequestration Exporting Terrestrial Ghg Accounting To The Deep Sea Ghg And Carbon Accounting Auditing Management Training Greenhouse Gas Management Institute
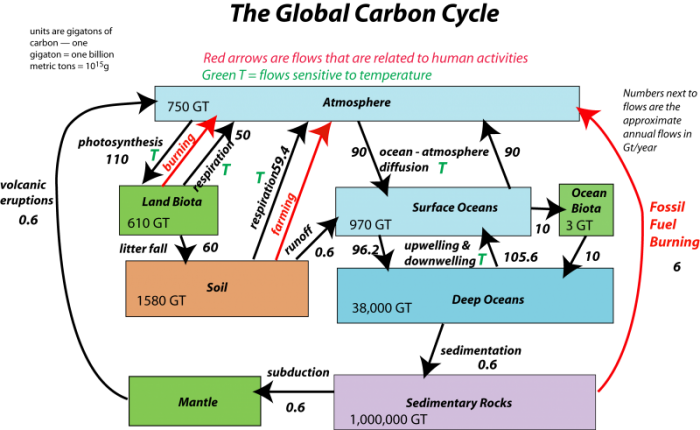
Overview Of The Carbon Cycle From A Systems Perspective Earth 103 Earth In The Future

Global Carbon Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
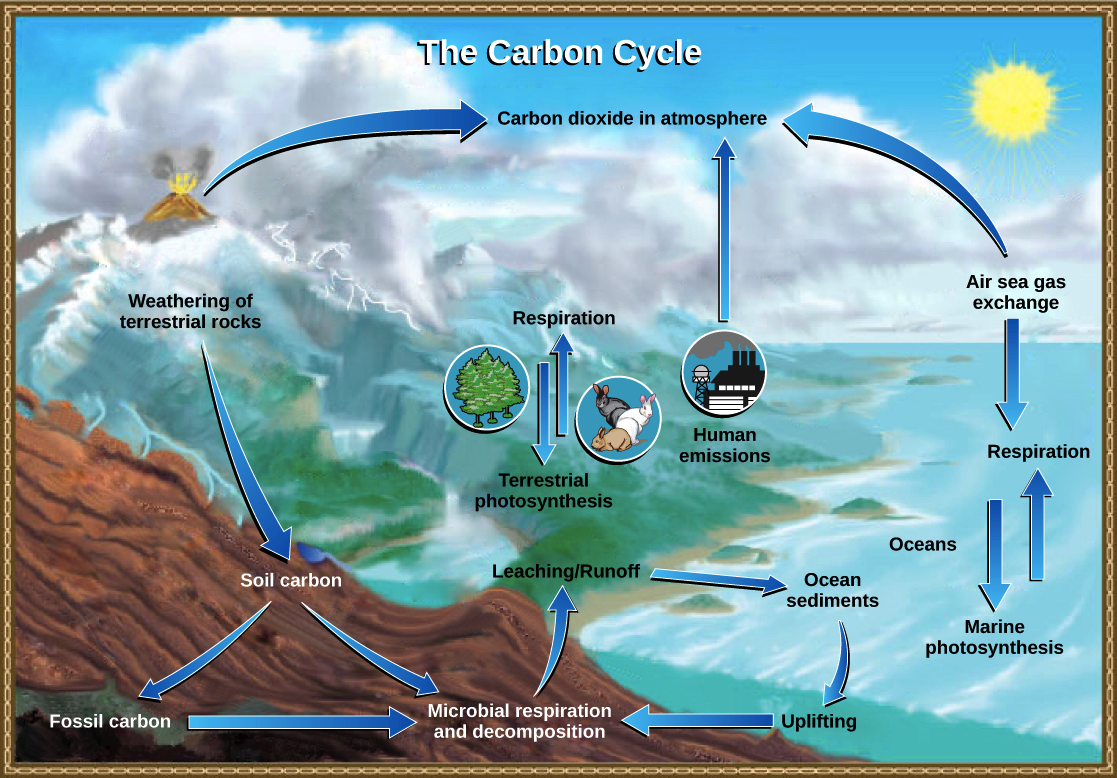
The Carbon Cycle Article Ecology Khan Academy

This Bedroom Storage Piece Represents A Chic New Take On Modern Luxury Simple Structured Lines Look E Lexington Home Lexington Furniture Designer Nightstand
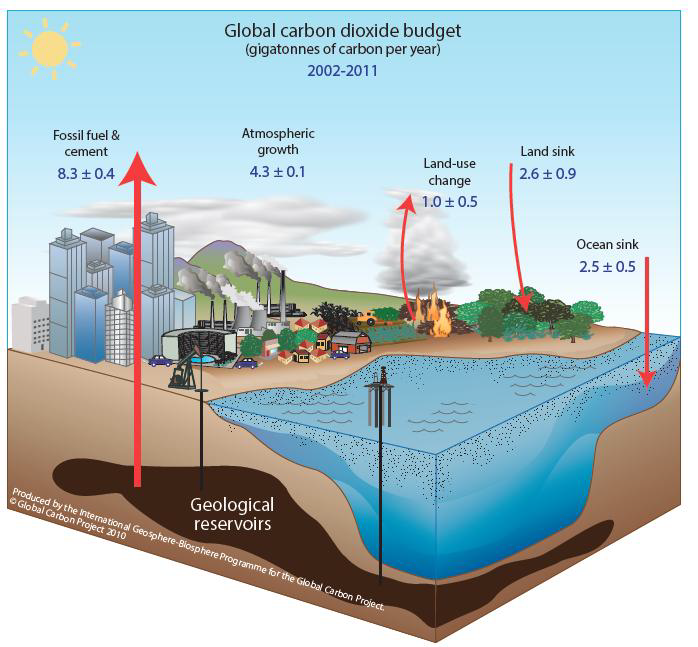
What Is The Carbon Cycle What Is The Science Behind It United States Carbon Cycle Science Program

Average Shelf Life Of Dehydrated Foods From Colleen Bohrer Dehydratedfoodshelflife Dehydrator Freeze Drying Food Food Shelf Life
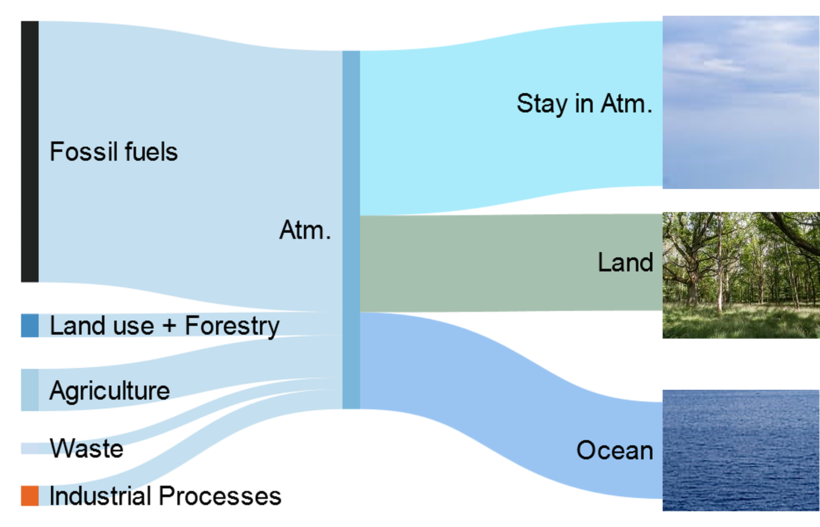

Comments
Post a Comment